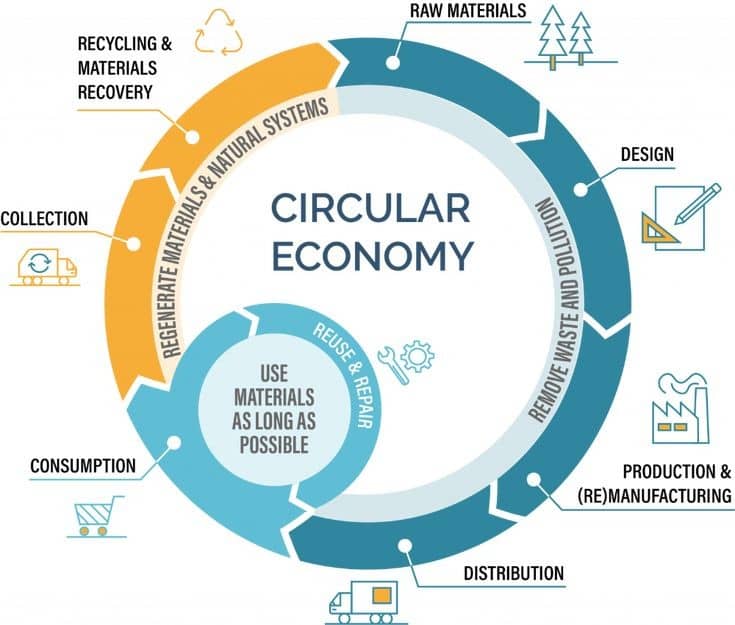
The circular economy is an economic system that aims to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and promote sustainable development. It is a departure from the traditional linear economy, which follows a "take-make-dispose" model, where resources are extracted, transformed into products, and eventually discarded as waste. In contrast, the circular economy seeks to create a closed-loop system where resources are kept in use for as long as possible through recycling, reuse, and regeneration.
Key principles of the circular economy include:
Design for durability and longevity:
Products are designed to be durable, repairable, and upgradeable. This extends their lifespan and reduces the need for frequent replacements. It also encourages the use of high-quality materials that can be easily recovered and recycled.Resource efficiency and waste reduction:
The circular economy emphasizes the efficient use of resources throughout the entire lifecycle of a product. This involves reducing material inputs, optimizing production processes, and minimizing waste generation. It also promotes the concept of "cascading," where waste from one process becomes a valuable input for another.Reuse and refurbishment:
Rather than discarding products after use, the circular economy promotes their reuse and refurbishment. This can involve repairing, upgrading, or repurposing products to extend their lifespan and maximize their value. Examples include second-hand markets, refurbishing electronics, and remanufacturing.Recycling and material recovery:
When products reach the end of their useful life, the circular economy aims to recover and recycle materials to create new products. This involves implementing efficient recycling systems, designing products with recyclability in mind, and creating markets for recycled materials. Advanced technologies like chemical recycling and material separation techniques are also being developed to improve recycling rates.Renewable energy and regenerative systems:
The circular economy promotes the use of renewable energy sources to power production processes and reduce dependence on finite fossil fuels. It also encourages regenerative systems that replenish and restore natural resources, such as regenerative agriculture and sustainable forestry.
Benefits of the circular economy:
Resource conservation:
By keeping resources in use for longer and reducing waste generation, the circular economy helps conserve natural resources, including raw materials, water, and energy.Environmental protection:
The circular economy reduces the environmental impact associated with resource extraction, manufacturing, and waste disposal. It minimizes pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and the depletion of ecosystems.Economic opportunities:
Transitioning to a circular economy can create new business opportunities, such as repair services, recycling facilities, and remanufacturing industries. It can also drive innovation in product design, materials, and technologies.Job creation:
The circular economy has the potential to generate new jobs, particularly in sectors like recycling, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture. It can also contribute to local economic development and resilience.Improved resilience:
he circular economy reduces dependence on finite resources, making economies more resilient to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. It also fosters greater self-sufficiency by promoting local production and resource recovery.
Challenges and considerations:
Systemic change:
Transitioning to a circular economy requires a shift in mindset, business models, and policy frameworks. It necessitates collaboration between various stakeholders, including businesses, governments, consumers, and civil society.Technological and infrastructural barriers:
Implementing circular economy practices may require the development of new technologies, infrastructure, and logistical systems. Investment in research and development is crucial to overcome these barriers.Consumer behavior:
Encouraging consumers to embrace the principles of the circular economy, such as repairing and reusing products, may require education and awareness campaigns. Consumers need to be willing to change their buying habits and prioritize sustainable options.Policy support:
Governments play a vital role in driving the transition to a circular economy by implementing supportive policies.